The moment a pregnancy test reveals its positive sign, a ripple of joy, anticipation, and perhaps a touch of nervous excitement spreads through the expectant parents and their circle of loved ones. It’s not just a confirmation; it’s the beginning of a journey filled with hopes and dreams. Family and friends rally around, creating a fortress of support. Their collective prayers and well-wishes become a shield of positivity. From ensuring the mother receives adequate nutrition to meticulously following medical advice, every step is taken to foster a healthy environment. As the due date approaches, the atmosphere is charged with a blend of excitement and trepidation. In these moments, every heartbeat, every kick, is a reminder of the shared prayers for a safe passage into the world.
WHAT IS A HIGH-RISK PREGNANCY?
A high-risk pregnancy refers to a situation where the health of the mother, the baby, or both is at an increased risk of complications before, during, or after childbirth. Various factors contribute to the classification of a pregnancy as high-risk, and these can be related to the mother’s health, the baby’s health, or external environmental factors. Maternal factors include pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease. Age is also a significant factor, with both very young mothers (teenagers) and older mothers (typically those over 35) facing higher risks. Multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets, are inherently high-risk due to the increased demands on the mother’s body. Fetal factors involve complications with the health of the baby, such as genetic disorders or developmental abnormalities. Infections during pregnancy, exposure to harmful substances, or issues with the placenta can also contribute to a high-risk designation. Environmental factors may include lifestyle choices, such as smoking or substance abuse, which can significantly impact the health of both the mother and the developing baby. Lack of prenatal care or inadequate medical attention can exacerbate the risks.
Higher-risk pregnancy requires vigilant supervision and tailored medical attention. This often includes more frequent prenatal visits, advanced diagnostic tests, and consultations with specialists. The goal is to identify and address potential complications as early as possible to optimize outcomes for both mother and baby. Despite the increased risks, many high-risk pregnancies result in successful, healthy deliveries with proper medical management and support. Open communication between the expectant mother and her doctors are crucial to navigating the complexities of a higher risk pregnancy, ensuring the best possible outcome for both the mother and the baby.
HOW SCANNING CENTRES SUPPORT
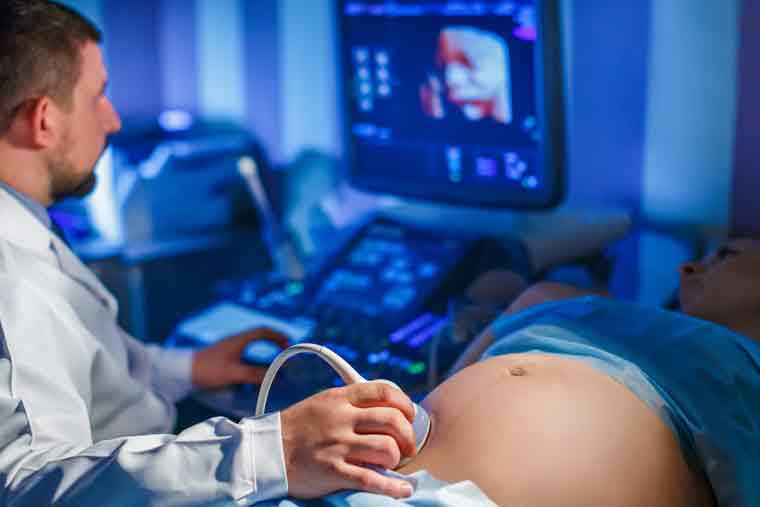
Monitoring high-risk pregnancies is a critical aspect of prenatal care, and scanning centres play a pivotal role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Through advanced imaging technologies and specialized procedures, these centres provide valuable insights that help doctors manage and mitigate potential complications associated with high-risk pregnancies.
Early Detection and Diagnosis:
Scanning centers employ a range of imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, to detect and diagnose potential issues early in pregnancy. Early detection is particularly crucial in high-risk pregnancies, where conditions like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or fetal abnormalities may pose increased risks. Ultrasound imaging allows doctors to visualize the developing fetus, assess its growth, and identify any structural abnormalities that may require additional attention or intervention.
Fetal Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring of the fetus is essential in high-risk pregnancy. Non-stress tests (NST) and biophysical profiles (BPP) are common methods to evaluate the well-being of the baby. NST measures the fetal heart rate in response to its movements, providing insights into the baby’s nervous system and oxygenation. BPP assesses various fetal activities, including movement, muscle tone, and the quantity of amniotic fluid. These tests help doctors gauge the overall health of the fetus and make informed decisions regarding the management of the pregnancy.
Doppler Ultrasound for Blood Flow Assessment:
High-risk pregnancies often involve concerns about blood flow to the placenta and the developing fetus. Doppler ultrasound is a specialized technique used in scanning centres to assess blood flow in the uterine and fetal vessels. Abnormal blood flow patterns may indicate conditions like intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or preeclampsia, allowing healthcare providers to intervene and manage these complications in a timely manner.
3D and 4D Ultrasound for Detailed Visualization:
In certain high-risk pregnancies, detailed anatomical information is crucial for diagnosis and planning. 3D and 4D ultrasound technologies provide enhanced visualization of the fetus, allowing doctors to examine specific structures in more detail. This can be particularly valuable in cases where there are concerns about fetal development or structural anomalies that may require specialized care.
Genetic Screening and Counseling:
Some high-risk pregnancies involve a higher likelihood of genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities. Scanning centres offer genetic screening and counselling services to assess the risk and provide families with information about potential genetic conditions. Techniques like chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis may be performed to obtain genetic material for analysis, enabling healthcare providers to offer informed guidance to parents and make decisions about the management of the pregnancy.

Advanced Imaging Modalities:
In complex cases, scanning centres may utilize advanced imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide detailed images of the fetus and surrounding structures. This can be particularly helpful in cases where traditional ultrasound may not provide sufficient information, allowing doctors to better understand and address specific challenges associated with high-risk pregnancies.
Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine:
Advancements in technology have facilitated remote monitoring of high-risk pregnancies. Telemedicine platforms allow doctors to review imaging results, conduct virtual consultations, and collaborate with specialists, providing timely and comprehensive care to expectant mothers, even in remote or underserved areas.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
Scanning centres are often part of a broader healthcare network that includes specialists in maternal-fetal medicine, neonatology, and other relevant fields. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that high-risk pregnancies receive comprehensive care, with different specialists collaborating to address specific challenges and optimize outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Ambady Scan Centre the pregnancy scanning centre in Thrissur plays a pivotal role in monitoring high-risk pregnancies, offering unparalleled early detection, detailed visualization, and continuous assessment of the developing fetus. Leveraging advanced imaging technologies and state-of-the-art facilities, Ambady Scan Centre ensures a comprehensive approach to managing expectant mothers facing heightened risks. With expertise in genetic screening and a commitment to multidisciplinary collaboration, for the past 25 years’ experience Ambady Scan Centre stands as a beacon of excellence in providing the best possible care for both the mother and the baby during high-risk pregnancies. In Thrissur and beyond, Ambady Scan Centre remains at the forefront of ensuring the health and well-being of expectant mothers.



